News
Best Malware Removal & Protection Software for 2021
Posted in: anti-malware, anti-malware software, anti-malware solutions, anti-virus/malware, avast, AVG, BitDefender, Cisco Umbrella, ESET, IT Strategy, malware, malware protection, Malware Removal Tool, malware threats, McAfee, Norton, Security - Sep 09, 2021
As a member of Senior IT, you want to select the best malware protection software for your organization. Whether it’s a zero-day exploit via adware, an attempted ransomware lockdown, or a trojan horse trying to run amok on your network, you want these malware bandits to be neutralized as fast as possible.
Time is of the essence to mitigate risk. The goal of malware protection tools is identifying suspicious files such as adware, keyloggers, spyware, trojan horses, worms, and viruses to quickly minimize potential damage to a business network’s devices. Malware is popular among cybercriminals and a constant threat, as it’s used to gain leverage over businesses for financial gain.
Table of Contents
- Malware Protection Software Comparison
- Best Malware Removal & Protection Software
- How Malware Protection Tools Work
- Malware Protection Software Features
- Select the Best Malware Protection Software for Your Business
Malware Protection Software Comparison
| Vendor | Cloud-Based Protection | VPN Service | Adware Protection | Compatibility with PC, Mac, Android & iOS | Business Size |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cisco Umbrella with Secure Endpoint |  |  |  |  | Midsize to Large |
| Avast CloudCare |  |  |  |  | Midsize to Large |
| AVG Antivirus Business Edition |  |  |  |  | Small to Midsize |
| ESET PROTECT |  |  |  |  | Small to Midsize |
| Bitdefender GravityZone |  |  |  |  | Small to Midsize |
| McAfee MVISION Cloud |  |  |  |  | Midsize to Large |
| Norton Small Business |  |  |  |  | Small |
Remote and hybrid work environments are more prevalent today than ever. The need to protect an organization’s endpoint devices from malware attacks is essential. The comparison chart above lists a few of the many cloud-based malware protection tools available; each can provide remote malware protection as if the laptop were physically connected to the business network. When compiling our list of the best malware protection software, we included solutions appropriate for small, midsize, and large businesses.
Any malware protection software that did not offer USB scanning or scheduled scanning was not considered for review. Remote work locations offer an increased potential to introduce malware via the USB port; therefore, scanning a USB connected device at any time is paramount to minimizing any possible malware attack. The malware vendors we selected are strong candidates for protecting your network, with slight variations in the services offered based on your individual needs.
Read more: VPNs, Zero Trust Network Access, and the Evolution of Secure Remote Work
Best Malware Removal & Protection Software
CISCO Umbrella
Cisco Umbrella protection starts with internet infrastructure devices, which are the network devices, web servers, internet servers, and transmission media to connect computers. Cisco Umbrella attempts to prevent any malware from penetrating the network at the frontline, internet infrastructure level using its interactive threat intelligence data.
Combining Cisco Umbrella with Cisco Secure Endpoint makes it a comprehensive business malware protection package. Secure Endpoint adds another layer of protection, should the malware get to any endpoint device. Secure Endpoint provides malware protection to cell phones, tablets, desktops, and laptops connected to the business network or remotely through the cloud.
Endpoint protection continually communicates with the most updated intelligence to mitigate any potential malware threats on endpoint devices. This comprehensive malware protection bundle is designed for large organizations, but very capable of supporting the midsize and small organizations that can afford it.
Avast CloudCare
Avast CloudCare offers a total cloud-based malware protection package with a couple of additional features. Avast adds an additional level of encryption for passwords you want to protect, along with a WiFi inspection. That tool scans your computer to minimize the chances of malware infiltrating a computer or network.
Avast advertises its product for small businesses with a hundred employees or less, but it also says its CloudCare solution can support up to a thousand devices globally. Avast’s key features are customizable data protection modules and an updated application control interface.
Avast uses a concept called behavior, web, and email, shields to protect businesses against suspicious requests or malicious emails. Also, Avast employs a data shredder that overwrites any deleted files — making it impossible for anyone to recover files in a data breach. SharePoint safeguarding is used to scan for malware on any uploads or downloads on business servers. Evaluators of the CloudCare solution liked the anti-spam capabilities for email, the WiFi inspector, and the ability to remove bad plugins.
AVG Antivirus Business Edition
A key feature of AVG is its built-in artificial intelligence (AI) that detects and prevents a malware outbreak to the network. AVG uses behavioral analysis with statistical testing to provide ransomware protection.
Another advertised feature of AVG is that this antivirus software provides identity protection. This product is designed for small businesses; it’s suitable for any small business that needs to protect clients’ personal information. The AVG cloud management console allows a business owner to remotely monitor threats, schedule scans or updates, and protect devices.
The ability to remotely manage devices is what evaluators liked most about AVG cloud solutions. The evaluators also complimented the safety rankings displayed for each web page opened.
ESET PROTECT
ESET provides malware protection services for small to midsize businesses. ESET addresses cybersecurity in a twofold process, offering cybersecurity training and a cloud-based malware protection solution. ESET recognizes that human error contributes to over 90% of malware breaches and thus offers extensive cybersecurity awareness online training.
Senior IT management can invest $1,625 to train 100 employees on cybersecurity best practices. Combining the user training with an ESET cloud-based malware protection solution is a good starting point for a business looking to improve its cybersecurity posture.
Some cybersecurity experts describe ESET as good, but not a top-of-the line cybersecurity solution. ESET is known to provide reliable detection against malware, and it’s touted as being effective against zero-day attacks. ESET’s Host Intruder Prevention System (HIPS) module has shown to be very reliable at recognizing ransomware attacks and neutralizing them. Further, ESET’s user-friendly graphical user interface (GUI) makes it easy to use and set up.
Bitdefender GravityZone
Bitdefender is reviewed as one of the better malware protection solutions. This vendor’s package creates several layers of protection before malware can attack a computer or server. Bitdefender uses risk analytics to highlight a device’s vulnerability to malware. From this same risk management dashboard, a cyber-technician can make changes to configuration settings to reduce device vulnerabilities.
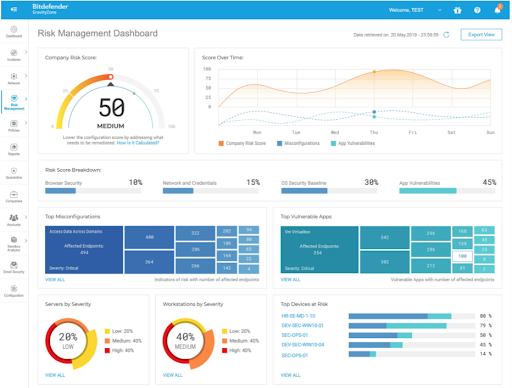
Bitdefender features advanced threat prevention that minimizes the need for manual intervention. The advanced threat security (ATS) module is an add-on that provides an additional method to discover hard-to-detect malware. ATS contains three sub-modules all designed to stop malware from fully executing:
- HyperDetect: Uses machine learning to stop malware attacks before execution
- Fileless Attack Defense: Inspects command code in memory, and prevents code from executing scripts using PowerShell or the Command prompt
- Sandbox Analyzer: Fully executes malware files to be used in identifying other similar malware files
Evaluators of Bitdefender GravityZone like the easy-to-use interface, and the ability to manage user access to web sites and applications.
McAfee MVISION Cloud
McAfee has expanded its services well beyond the typical antivirus software for home use. McAfee MVISION Cloud services allow a business to manage its cloud-based applications across multiple cloud computing services, such as Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS).

MVISION is a multi-cloud management solution that can enforce policies based on business content rules. Once MVISION is implemented, it can protect against any cloud threats across all cloud computing services. MVISION is omnipresent for a business network on any cloud computing service, with the ability to take control over data or cloud activity from any console.
MVISION can identify any potential insider threat through machine learning, as well as identifying suspicious user behavior. This McAfee product can identify inactive accounts or an account with elevated access that is not needed by the account holder. Based on behavior analysis, MVISION can identify malware and initiate on-demand scanning using real-time historical data to determine if the file is malware. McAfee’s MVISION has a plethora of state-of-the-art cloud options, making it very attractive for managing cloud-based business transactions.
Norton Small Business
Norton is a popular antivirus software package among consumers, but its business solution is also attractive. Norton Small Business reviews state it’s a very effective malware protection solution. For instance, Norton has a “find device” feature that can send alarms when a mobile phone or iPad is misplaced, pinpointing a user’s lost devices. With remote lock or wipe, Norton can prevent data on Android phones from being compromised.

The Norton Small Business package can support up to 20 devices at a reasonable cost. Norton helps keep costs low for small businesses by prorating the price for any new devices added throughout the annual cycle. Norton’s web-based management portal allows you to see all registered devices and identify any devices at risk. The Norton Small Business solution had favorable features and positive feedback from evaluators.
How Do Malware Protection Tools Work?
To identify and remove malware, malware protection tools use three methods. First, Malware protection tools can use a definition file, known as a blacklist or malware signatures. The malware protection software then compares suspicious files against known operational behavior of files on the blacklist. It then flags the suspicious file for removal if the behaviors are the same. Antivirus also uses a similar signature-based detection to identify suspicious files.
The second malware protection methodology uses heuristics, or behavioral analysis, to identify suspicious files. A file can be identified as suspicious if it behaves in a manner that exhibits malware behavior, such as removing important files from a networked device. Anti-malware can isolate a file it has never seen before; conversely, antivirus software can never isolate a threat it has never before seen. The downside to heuristics is it can give false positives.
The last anti-malware method is called sandboxing, where a suspicious file is moved to a sandbox for further observation to determine if it’s malware.
Malware Protection Software Features
Good malware protection tools provide the following protections for business devices:
- Real-time malware protection: Any time a file is accessed, the file is scanned.
- Vulnerability protection profiles: Prevents malware from exploiting system vulnerabilities and gaining access to devices. It also protects against illegal code execution and buffer overflows.
- Scheduled scans: Flexibility to do impromptu scans helps mitigate potential zero-day attacks. Additional scanning options can be narrowing down to a specific file size, or excluding certain file extensions from being scanned.
- Protecting remote devices: The software can issue password change reminders, use data encryption, test security, and limit data access to essential personnel only.
- Anti-phishing protection: Software packages can contribute to employee education, as well as blocking suspicious emails and scanning email for any malicious content.
Select the Best Malware Protection Software for Your Business
As you can tell, many of the good malware protection tools provide similar functionality to protect the network and its devices. One easy selection criterion is determining the number of employees or devices requiring protection. Another is cost.
What is a business willing to pay for a good malware protection tool? Identify your cybersecurity requirement in its totality, and then Senior IT needs to invest the dollar amount needed to meet that defined requirement.
Read next: Top Cyber Security Threats to Organizations
The post Best Malware Removal & Protection Software for 2021 appeared first on CIO Insight.
topIaaS vs PaaS: Compare Cloud Service Models
Posted in: cloud infrastructure platform, cloud platforms, Cloud Virtualization, IaaS, infrastructure-as-a-service, PaaS, platform-as-a-service - Sep 08, 2021
Cloud computing services are becoming mandatory parts of the modern business world. Most organizations are using one or more types of cloud-based services, whether that’s Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS), Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS), or Software-as-a-Service (SaaS).
SaaS is the most common model among cloud computing services, but IaaS and PaaS serve equally important functions for businesses. IaaS and PaaS facilitate the demand of end users to collect, store, and process a large amount of data. In this article, we discuss IaaS vs PaaS for a better understanding of these cloud-based services.
Read more: Creating a Cloud Strategy: Tips for Success
What Is IaaS?
Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS) is a form of cloud computing that provides virtualized computing resources to consumers over the internet on a pay-as-you-go and on-demand basis. These virtualized resources include essential computing, storage, and networking resources.
IaaS helps consumers gain real-time business insights without the higher maintenance costs of on-premises data centers and hardware. IaaS gives users the flexibility to scale IT resources up and down as needed.
It also helps users quickly provision new applications and increase the reliability of underlying infrastructure. IaaS is easier to use, faster, more flexible, and cost-efficient. The cloud provider manages IT infrastructure, delivering services to subscriber organizations through virtual machines accessible over the internet.
When Should You Use IaaS?
IaaS is an alternative to on-premises infrastructure that specifically helps network architects and system administrators. Here are the primary use cases for IaaS:
- You want to have control. With IaaS, providers manage servers and storage, but your organization gets to manage everything running on the infrastructure.
- Your company is growing. With IaaS, you can make changes as your needs evolve, or depending on traffic spikes and valleys.
- You want to increase your stability, reliability, support, and security. With IaaS, there’s no need to maintain and upgrade hardware, or troubleshoot equipment problems.
Examples of IaaS providers include:
Amazon EC2
Compute Engine
Linode
Azure Virtual Machines
DigitalOcean
Virtual Machine Manager
Alibaba Elastic Compute Service
Hostwinds
OVHcloud
Alibaba E-HPC
Read more on ServerWatch: Best Cloud-Based Services & Companies

What Is PaaS?
Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS) is a category of cloud computing that provides users a complete cloud-based platform for developing, running, and managing their applications. These services are typically associated with developing and launching applications, allowing developers to build, maintain, and package such software bundles.
In PaaS, a third-party provider delivers hardware, software tools, and infrastructure to users over the internet. Usually, these are used for application development. Users can purchase the resources as needed from a service provider on a pay-as-you-go basis, accessing them over a secure internet network. The users manage the applications and services they develop, and the cloud service provider typically manages everything else.
When Should You Use PaaS?
PaaS is an alternative to traditional hardware and software development tools to help developers and deployment. PaaS use cases include:
- You need to build software, and you have resources. If you don’t want the trouble of building servers, networks, and managing databases. In this situation, PaaS facilitates the virtual platforms and tools to create, test, and deploy your applications and services.
- Multiple remote developers are working on the same project. PaaS can provide you with a great environment, speed, and flexibility for your entire process, regardless of where your developers are located.
- You are rapidly developing or deploying an application. PaaS can help reduce costs and simplify the challenges associated with quickly shipping an application.
Examples of PaaS providers include:
- AWS Elastic Beanstalk
- Oracle Cloud Platform
- Google App Engine
- Microsoft Azure
- Salesforce aPaaS
- RedHat OpenShift
- Mendix aPaaS
- IBM Cloud Platform
- SAP Cloud Platform
- Engine Yard
IaaS vs PaaS: What’s the Difference?
IaaS and PaaS are both cloud-based options designed to relieve the company and IT department of their responsibilities when it comes to handling data, software, OS, virtualization, servers, storage, and networking. However, there are several differences when considering IaaS vs PaaS.
Services
An IaaS provider offers a virtual data center to store company information and create platforms for services and application development, testing, and deployment. On the other hand, a PaaS provider offers a virtual platform and the tools to create, test, and deploy applications and services.
End-User Management
IaaS allows end users to manage their applications, the platforms used to build them, and the cloud-based resources to keep everything running — such as OS, middleware, runtime environment, applications, and data. On the other hand, PaaS allows end users to manage the apps they develop with the tools provided by the cloud platform.
End User Security Responsibilities
The IaaS users are responsible for securing their data, user access, applications, operating systems, and virtual network traffic. On the other hand, the PaaS users are responsible for securing their applications, data, and user access.
Vendor Security Responsibilities
The IaaS vendors are responsible for enforcing secure access controls to the physical facilities, IT systems, and cloud services. On the other hand, the PaaS vendors are responsible for securing the operating system and physical infrastructure.
Flexibility and Cost
IaaS is very flexible, but it’s the most expensive form of cloud computing. On the other hand, PaaS is flexible within certain limitations, and mid-tier in cost.
Choosing the Right Solution
The biggest advantage of IaaS is that solutions can easily scale with businesses as they grow, or downsize if necessary. On the other hand, the biggest advantage of PaaS is its ability to save developers significant time throughout a project.
In cloud computing, IaaS is often the first step in hybrid-cloud and multi-cloud strategies, whereas PaaS is a step toward Infrastructure as Code. IaaS and PaaS are designed to achieve different goals for different types of users. When it comes to IaaS vs. PaaS, depending on your organization’s needs you may not have to choose.
Read next: Cloud Computing Thinks Small (and Medium Sized Business)
The post IaaS vs PaaS: Compare Cloud Service Models appeared first on CIO Insight.
topAccess Control Security Best Practices
Posted in: access control, access management, best practices, biometric authentication, Cloud Access Manager, cloud data security, IT Strategy, mfa, Network Access Control, physical security, remote access, Security, security best practices, SSO - Sep 07, 2021Access control security measures ensure only authorized users are able to enter and interact with a network. You wouldn’t want just anyone to be able to view sensitive information on one of your company’s laptops. Alternatively, you may want only certain users or roles within the organization to have access to sensitive information.
There are four different types of access control: DAC, MAC, RBAC, and ABAC. As such, the access control security best practices for your organization depend on the company size, level of security, and any compliance regulations.
Read more: VPNs, Zero Trust Network Access, and the Evolution of Secure Remote Work
Types of Access Control
The types of access control can be broken down into who administers access (DAC and MAC) versus how access is administered (RBAC and ABAC).
Discretionary Access Control (DAC)
In DAC, one or more system administrators grant each user a certain level of access according to their role. This method most likely works best for smaller companies that can rely on individuals to regulate access.
Mandatory Access Control (MAC)
The government and military often employ MAC. In this method, a central agency gives individuals information clearance based on what they level they are working in. It is non-discretionary, in the sense that one person is not in control of granting each person a certain kind of access. MAC is more centralized and standardized.
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
As the name implies, only individuals who play a particular role within an organization will need access to certain data in the RBAC model. For instance, an HR administrator will need different information than the CFO; they will thus have access to different types of data in the network.
Attribute-Based Access Control (ABAC)
In contrast to RBAC, in ABAC the person’s role doesn’t matter as much as a set of criteria, such as their location or work shift. This method pertains most to multinational enterprises, where individuals are accessing information from various parts of the world and at different times.
Applications of Access Control
There are two types of access control applications: data access control and physical access control. Your company will likely need both, unless it completely operates remotely. In that case, your focus will be data access control. Each type of access control employs different forms of entry access: login credentials, badge scanners, biometric technology, or a combination of these.
Cloud-Based Access Control
An organization can store data on a local server (legacy systems), in a cloud, in multiple clouds, or in a mix of physical data storage and cloud storage (hybrid). Most companies these days store their data in hybrid or completely cloud-based environments. Cloud-based storage offers a more secure and convenient way of configuring access control, as it easily integrates with other software.
Cloud-based storage offers a more secure and convenient way of configuring access control.
For example, an on-site system administrator can configure access for users via a cloud access security broker. Within this cloud-based control panel, the system administrator sets who can log into a SaaS application, such as Box or Workday, through single sign-on (SSO).
As mentioned before, login access can take many forms, from entering passwords to scanning fingerprints or badges. The system administrator grants or denies access by adding layers of security between the user’s web browser or desktop app and the SaaS cloud server. The system administrator can permit or deny access to particular URLs or to particular categories, such as job boards or social media.
At a more granular level, the system administrator can allow a user access to a SaaS, but still permit only certain functions to be performed in the SaaS. The user, whether signing in via the installed app or via web browser, will then either be allowed, blocked, or redirected.
Physical Access Control
Allowing only certain people to enter the physical premises is still a prevalent security concern for enterprises with brick-and-mortar locations. A system administrator can grant access to certain users through badges, key fobs, keypads, biometric technology, wireless access control, or mobile access control.
There are many types of biometric technology that are becoming increasingly popular for enterprise access control. These devices store and read biological data, such as fingerprints, retina or iris scans, or facial features. Some methods are more secure and expensive than others. Based on your company’s needs, you’ll have to consider whether biometric technology is worth implementing.
Read more: Is Biometric Technology Worth the Cost?
In wireless access control, the user presents some sort of login credential, such as a PIN. A wireless router communicates between the control panel, the reader, and the barrier to entry — such as a lock, gate, or door.
In mobile access control, the user opens the downloaded mobile app on their mobile device. The app then communicates with the reader to allow physical entry.
Access Control Tips and Best Practices
For data access control, cloud-based is the way to go because it:
- Is more secure
- Is convenient
- Saves money
- Saves time
- Keeps everything up-to-date
Convenience is a key benefit with cloud data access control, as your system administrator does not have to be located in any particular physical place to configure data access control. Further, everything will be kept up-to-date because the server automatically backs up information.
For physical entry access control, mobile apps are your best bet because they are:
- More foolproof
- More secure
- Very convenient
Users are likely to lose, forget, or damage their badges or key fobs. You also don’t want to risk those physical objects landing in the wrong hands, and have an unauthorized person enter the property. Your company may also want to consider using biometric technology, but will have to weigh the privacy and ethics concerns of storing and managing users’ biological data.
If confidential or sensitive data gets leaked or hacked, your company could face fines, damage to its reputation, and other negative consequences. This is why access control is so important and prevalent today in enterprises big and small.
Read next: What Does a Next Generation Firewall Do?
The post Access Control Security Best Practices appeared first on CIO Insight.
topData Analytics vs Data Science: What’s the Difference?
Posted in: Big Data, big data analytics, Big Data careers, big data science, Careers, Data Analytics, data science - Sep 07, 2021In today’s big data world, insights produce actionable results. But with big data comes the need for a greater understanding of the tools required to glean as much information as possible.
People who perform functions such as data analytics and data science help companies organize massive amounts of data and develop results-driven actions for the next steps. To help you optimize your data, let’s break down both categories, examining their differences and discovering how each provides value to business.
What Is Data Analytics?
Data analytics focuses on viewing the historical data. Analysts use datasets to learn information in specific areas, using specific software. For example, a data analyst may need to find out why a marketing campaign did well only in one region and nowhere else.
Read more: What Is Predictive Analytics?
What Is Data Science?
Data scientists focus on machine learning and predictive modeling. They use scientific methods to learn insights from both structured and unstructured information. Data scientists estimate the unknown by seeking answers to questions, writing algorithms, and building statistical models.
Data scientists can arrange fuzzy sets of data using multiple tools simultaneously, and also develop their own automation systems and frameworks.
Why Do These Topics Get Confused?
Sometimes technical terms get confused because the technology is constantly evolving. While the tasks performed by data analysts and data scientists are related, and some people use the terms interchangeably, they are unique fields that differ in many ways. One of the biggest differences is their scope.
Data scientists focus on the big picture, finding meaningful correlations between large datasets. People who work in data analytics help to uncover the specifics of these extracted insights.
If you think of data science as more of an umbrella term that data analytics sits under, it may help keep the two separated in your mind.
How Are Data Analytics and Data Science Used in Business?
Data Analytics
Data analytics help companies know customers in more depth. Knowing who their audience is allows a business to evaluate things like ad campaigns and personalized copy. As a result, data analytics helps create content strategies and develop products — improving a company’s bottom line by boosting performance.
A data analyst manages structured data, often using SQL queries for such purposes. Most hold at least a bachelor’s degree in data analytics, or have backgrounds in statistics and database administration. If they lack formal education, data analysts can learn the tools they would use in a practical work environment. Some of the skills tools required are statistical analysis, database management and reporting, data analysis, R or SAS, and SQL.
If you’re interested in becoming a data analyst, you should look within these fields:
- Finance
- Health care
- Travel
- Gaming
Data Science
A data scientist helps in summarizing the performance of the company, and the overall health of the product. They’ll analyze the businesses’ health, find problems, and show enterprises how to deal with them. Companies can then predict the success rate of their strategies by using data science.
Data scientists can be data engineers or big data architects. In addition to mathematical and statistical knowledge, hacking skills, and substantive expertise, many data scientists hold a master’s degree in data science.
Some tools and skills that data scientists rely on are machine learning, software development, Java, Hadoop, Python, and data mining/data warehousing. In addition, data scientists responsible for handling unstructured data use NoSQL.
If you’re interested in becoming a data scientist, you may want to seek out:
- Search engine engineering
- Machine learning
- AI
- Corporate analytics
Data Analytics vs Data Science
While data analytics and data science are interconnected, they each play a vital, but different, role in business. When it comes to data analytics vs data science, understanding how to best utilize each of them will help your business analyze trends and develop the correct solutions.
Read next: What Is Vector Similarity Search?
The post Data Analytics vs Data Science: What’s the Difference? appeared first on CIO Insight.
topWhat Is the Cost of Remote Work for Employees and Businesses?
Posted in: Blogs, Careers, Hiring, hiring challenges, HR Management, remote work - Sep 07, 2021The COVID-19 pandemic forced millions of people to begin working remotely, but what is the cost of remote work? Employees have adjusted to a new “normal” work environment, and companies have adapted to a “new” operational domain. A Glassdoor study shows job seeker interest in remote work remains high, but businesses are less interested.
What can each side, businesses and employees, do to help alleviate tensions between parties? It depends on one’s point of view. Business leaders, for the most part, want to bring employees back to the office. Remote employees want the flexibility remote work provides, and are demanding a better work-life balance. Is there any middle ground?
Read more: VPNs, Zero Trust Network Access, and the Evolution of Secure Remote Work
Employees Crave Flexibility
Before the pandemic, many organizations provided a “work from home” option to their employees. Although not widely used, employees already working from home provided a blueprint to handle a crisis like COVID-19.
Surprisingly, even companies with relatively small infrastructure were able to allow thousands of employees to continue working. With everyone remotely connected, all employees began to realize the potential remote work could offer, including flexible schedules, no commutes, and more family time.
40% of employees said their organization hasn’t communicated its vision for post-pandemic work.
In April 2021, McKinsey released a report outlining employees’ questions and concerns during and after the pandemic. The survey shows that remote employees are more productive and less anxious when a company takes the time to communicate expectations.
Unfortunately, 40% of employees surveyed said their organization hasn’t communicated its vision for post-pandemic work. Communication alleviates frustration and burnout; employees deserve to know what’s coming. After the crisis ends, 52% survey respondents said they want a more flexible working model.
Businesses Remain Skeptical of Remote Work
Many employees believe remote work saves their employers money, but companies want to cut pay to those workers who wish to continue remote work.
For example, Google wants to lower wages if an employee moves to an area with a lower cost of living. Before the pandemic, many companies’ pay was based on the location of a central office. When companies like Google and other big tech firms floated this idea, many employees felt betrayed and outraged.
These employees don’t want to take a pay cut because they move to a different location. It’s worth noting that employees who moved before the pandemic didn’t receive a pay cut. And when business leaders relocated, their salaries didn’t receive adjustments.
That said, depending on the type of work, businesses leaders have trouble believing remote employees are actually more productive. They say things like on-site workers are more innovative thanks to in-person chats with colleagues. However, recent evidence shows office employees actually tend to work with headphones and ignore each other.
Read more: Top 10 Paying IT Jobs in 2021
Business leaders also appeal to fairness. Many industries require people in specific business areas to be in the office, staffing call centers and manufacturing units. If these employees need to be there physically, the thinking goes, then so should the whole workforce.
As businesses threaten remote employees with pay cuts or layoffs, employees with new attitudes are leaving companies for full-time remote opportunities. As global demand for skilled workers — especially in technical fields — rises, employees believe they can demand more flexibility.
What’s more, some states are offering remote employees financial incentives to work there. Cities in states with a lower cost of living like Arkansas, Georgia, and Arizona offer stipends to people who want to work exclusively remote. Unfortunately, the incentive is just for the first year of work. It’s up to businesses to offer more long-term incentives to keep remote workers happy.
What the Future Holds
If the pandemic lasted a few months, these conversations wouldn’t be happening. As COVID-19 progressed, workers’ priorities shifted. Work will need to more flexible for both workers and businesses going forward. Recent outbreaks of the COVID-19 Delta variant are pushing out companies’ timelines to get employees back in the office.
The advantage, for now, is with remote employees looking for a more permanent remote work model. Business leaders trying to get these people back in the office face an uphill battle as long as the pandemic goes on. For the present, both sides need to think about the future, and how things can work differently.
Read next: Edge Computing: Tips for Hiring and Getting Hired
The post What Is the Cost of Remote Work for Employees and Businesses? appeared first on CIO Insight.
topDaman News and Events
This showcases our company news and upcoming events. Please check back as this page will change frequently.


